Permissioned Keys
Permissioned Keys provide a way for different traders to share the same account. Using this mechanism, the owner of an account can provide different types of permissions, allowing flexibility to what and what not the permissioned users can do with its account.
A permission, or set of permissions, is also known as an authenticator. See all available authenticator types here.
This section will guide you through authenticators use and management. We show the two sides of this authenticating interaction. We'll label the main user, which gives the permissiones, as the owner, and the permissioned user as the trader.
Owner
There are 2 ways to setup Permissioned API Keys: 1/ Via the Trade interface (default permissions to trade on all cross-margin pairs) 2/ Via API (customisable)
Setup Permissioned API Keys via Trade Interface
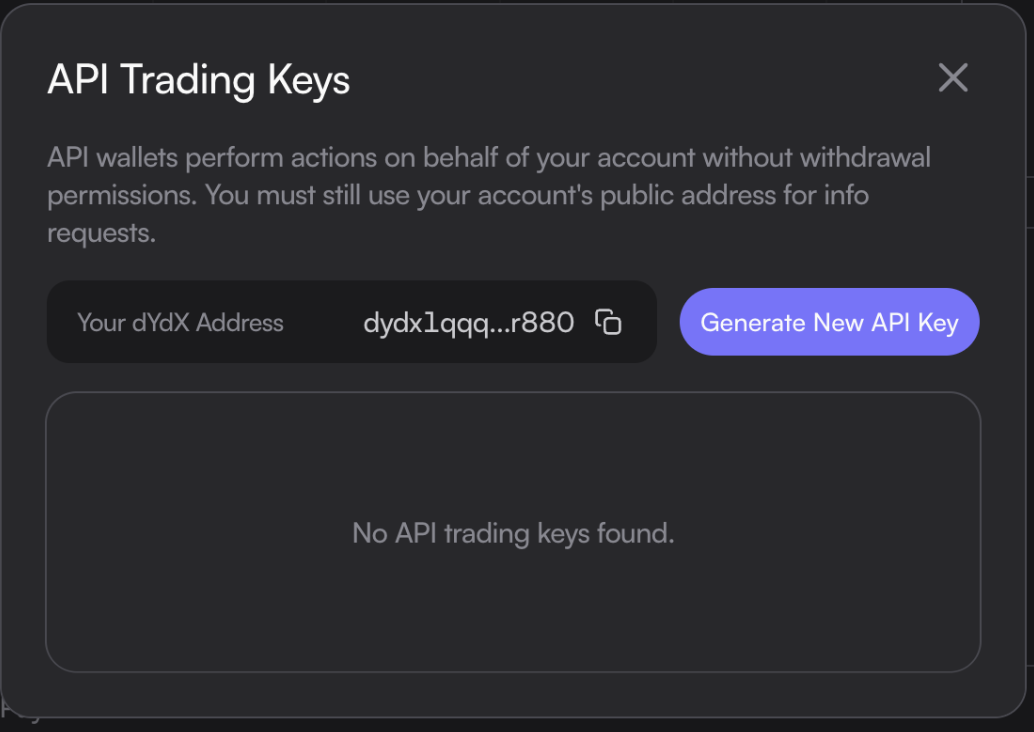
On the dYdX.trade, after signing in with your wallet or socials:
- click
More → API Trading Keys. - Click
Generate New API Key. This generates a new keypair:- API Wallet Address
- Private Key
- Check the
termsand clickAuthorize API Key. - Now you can go to Import private key to start trading via API keys.
Create an authenticator
Alternatively, you can create a custom authenticator which allows only the trader to place orders.
To create this authenticator, we use two sub-authenticators: signatureVerification and messageFilter:
- the
signatureVerificationauthenticator must be present in all authenticator sets and contains the trader's public key; - the
messageFilterauthenticator must contain the gRPC message ID of the allowed transaction (hereMsgPlaceOrder).
We compose everything together using the composable authenticator AllOf, stating that some trader's transaction is only allowed if it complies with all the authenticators.
The trader also needs to send the owner the its public key, associated with its address. This can be done by encoding the public key (e.g., hex string) and sending it. The owner then decodes it, serving it as input below.
# trader_key = trader_wallet.public_key.key
auth = Authenticator.compose(
# All sub-authenticators must be valid.
AuthenticatorType.AllOf,
[
# The allowed account.
Authenticator.signature_verification(trader_key),
# The allowed action.
Authenticator.message_filter("/dydxprotocol.clob.MsgPlaceOrder"),
],
)Add the authenticator
Now we need to push the authenticator to the network.
# Add the authenticator.
response = await node.add_authenticator(wallet, auth) List authenticators
You can confirm if the authenticator was added by listing all the authenticators associated with your (owner) address.
The added authenticator, identified by an ID (integer), will appear last on the list. The trader will then need to use this ID.
# List authenticators.
authenticators = await node.get_authenticators(wallet.address)
# Grab the last authenticator ID.
id = authenticators.account_authenticators[-1]Remove the authenticator
Authenticators can be removed if they are needed anymore, or if the trader goes rogue.
# Remove the authenticator.
response = await node.remove_authenticator(wallet, id)Trader
Get the authenticator ID and permissioned API Key
Grab the authenticatorId created by the owner in Add authenticator, either by:
- request the owner for the
authenticatorIdor by using the list authenticators method to fetch the to be used authenticator (see list authenticators). - Get the private key
DYDX_TEST_PRIVATE_KEYfrom the owner in via the Trade Interface.
Setup the permissioned wallet
If you got a private key from the trading interface load in via fromPrivateKey, otherwise use fromMnemonic if you didn't create via the trading interface by assigning to mnemonic.
const fromWallet = await LocalWallet.fromPrivateKey(DYDX_TEST_PRIVATE_KEY, BECH32_PREFIX);
const authenticatedSubaccount = SubaccountInfo.forPermissionedWallet(
fromWallet,
address, //owner dydx address
subaccountNumber, //subaccount to trade onbehalf of
[authenticatorId],
)Using the authenticator
The trader can now use the permissioned API key to perform the allowed trading actions.
In this example, the trader can use the authenticator to issue orders on the behalf of the owner.
const client = await CompositeClient.connect(network);
// Place an order using the authenticator.
const tx = await client.placeShortTermOrder(
authenticatedSubaccount,
'ETH-USD',
side,
price,
0.01,
clientId,
goodTilBlock,
timeInForce,
false,
undefined,
);